Beating ChatGPT-4o with a Local Model: Qwen 2.5 72B on a Single H200
Over the past week, I conducted a series of performance benchmarks to compare locally hosted large language models with cloud-based APIs in real-world automation tasks. What started as a simple experiment turned into an eye-opening result.
🧪 The Task
The benchmark involved a structured browser automation workflow: configuring a Volvo C40 Recharge on the Volvo Cars Australia website and completing an enquiry form, all driven by natural language instructions processed by the model.
⚔️ The Competitors
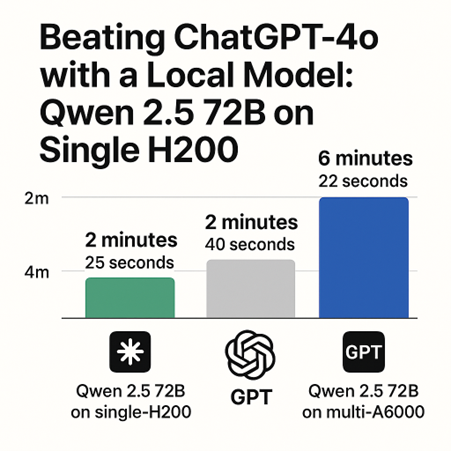
- Qwen 2.5 72B (Quantized) on a single NVIDIA H200
- ChatGPT-4o, accessed via OpenAI API
- Qwen 2.5 72B (Quantized) on a multi-GPU A6000 setup
⏱️ Results
|
Model |
Task Completion Time |
|
Qwen 2.5
72B on H200 |
2 minutes
25 seconds ✅ |
|
ChatGPT-4o
(API) |
2 minutes
40 seconds |
|
Qwen 2.5
72B on multi-A6000 |
6 minutes
22 seconds |
💡 Why Did the H200 Win?
The NVIDIA H200 significantly outperformed the other setups due to several key factors:
- High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM3e): With 141 GB of on-chip memory, the entire 72B model fits without the need for model parallelism or cross-device communication, eliminating synchronization overhead.
- Exceptional Memory Bandwidth: Approximately 5 TB/s bandwidth ensures that transformer layers remain fully saturated with weight data, reducing latency.
- Hopper-Class Transformer Engine: Accelerates quantized FP8/INT8 computations to near-FP16 speeds, enhancing inference performance.
- Single-GPU Simplicity: Avoids complexities associated with multi-GPU setups, such as NCCL overhead and PCIe latency, resulting in more efficient execution.
Collectively, these advantages led to 2.4× faster token generation compared to the same model running across multiple A6000s, and even surpassed the performance of ChatGPT-4o in this structured task.
🧠 Technical Insights
- Quantization Techniques: Leveraging INT8 quantization reduced the model size and improved inference speed without significant loss in accuracy.
- Model Deployment: The model was deployed using the Ollama framework, facilitating efficient local inference.
- Automation Tool: The use of browser-use enabled seamless browser automation through natural language instructions, showcasing the potential of AI-driven web interactions.
This experiment reinforces a key point: with the right hardware, local LLM deployment is not only viable—but can outperform cloud models in specific tasks. If you're exploring on-prem AI, edge inference, or real-time systems, don't underestimate the power of the H200 + quantised LLMs.
Feel free to connect if you're working on similar infrastructure or model optimization challenges—I’d love to exchange ideas.
#AI #LLM #H200 #InferenceOptimization #EdgeAI #Qwen #ChatGPT4o #Ollama #Transformers #Benchmarking #NVIDIA #BrowserAutomation
Automated Volvo car configuration



